December 14, 2021
物联网消息标准
#
官网
It is designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport that is ideal for connecting remote devices with a small code footprint and minimal network bandwidth.
极其轻量的发布/订阅消息传输,使用小量代码脚本和极小网络带宽来连接远程设备。
- 轻量
- 高效
- 双向
- 大规模(百万设备)
- 可靠
- 支持不可靠网络
- 安全
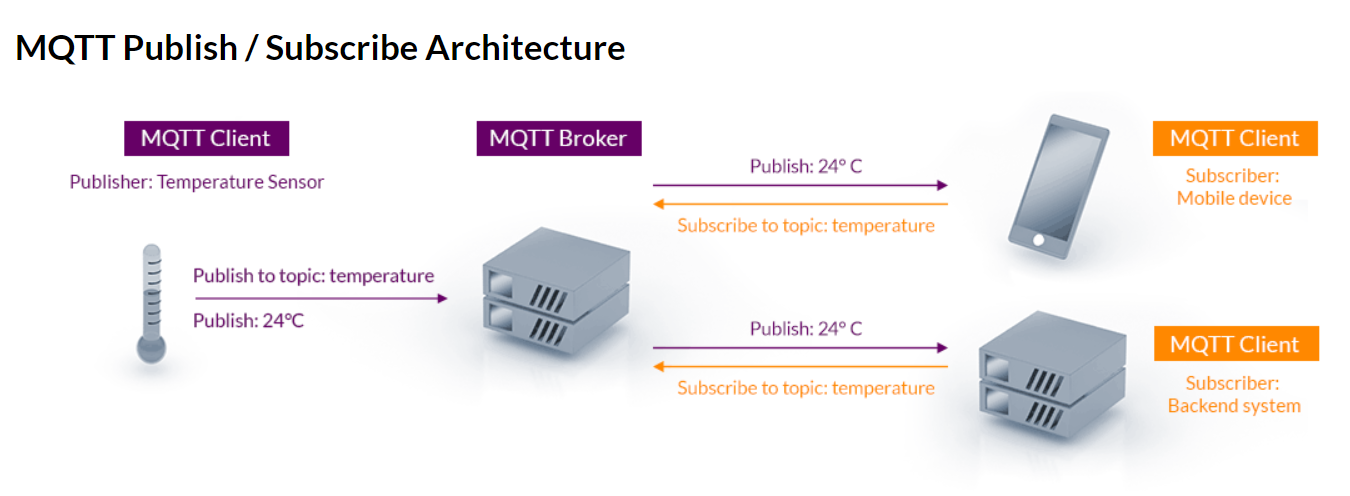
多个mqtt客户端连接到broker(译为:中间商),围绕topic来实现发布/订阅操作,某些客户端向topic发布消息,某些客户端订阅topic上的消息,当broker接收到某个topic上的消息时,它会将消息转发到订阅了该topic的客户端。
mqtt 5.0
QoS
#
Quality of Service
control traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications with limited network capacity
控制交通,确保有限网络容量下的应用性能。
QoS(Quality of Service,服务质量)指一个网络能够利用各种基础技术,为指定的网络通信提供更好的服务能力,是网络的一种安全机制, 是用来解决网络延迟和阻塞等问题的一种技术。QoS 的保证对于容量有限的网络来说是十分重要的,特别是对于流多媒体应用,例如 VoIP 和 IPTV 等,因为这些应用常常需要固定的传输率,对延时也比较敏感。
当网络发生拥塞的时候,所有的数据流都有可能被丢弃;为满足用户对不同应用不同服务质量的要求,就需要网络能根据用户的要求分配和调度资源,对不同的数据流提供不同的服务质量:
...
December 13, 2021
简单动态字符串
#
结构:
| len | alloc | flag | buf |
|---|
| 长度(已使用空间大小) | 分配(总共空间大小:buf 的大小减 1 – ‘\0’字符占用了 1) | 标记(sdshdr 的类型) | 真正存储字符串的地方 |
文件:
sds.h, sdsalloc.h, sds.c.
定义:
根据类型获取长度:
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
新建:
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
* If SDS_NOINIT is used, the buffer is left uninitialized;
*
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */ // sds的头部存储了它的长度
sds _sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen, int trymalloc) {
void *sh; // sds的header
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen); // 根据size大小返回类型
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type); // 根据类型返回header长度
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
size_t usable; // 可用的内存大小
assert(initlen + hdrlen + 1 > initlen); /* Catch size_t overflow */
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable); // 三元运算符,根据trymalloc的值选择用哪个alloc函数,分配后,还会标志可用内存大小
if (sh == NULL) return NULL; // 分配失败返回NULL
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen; // 将sh转为char*,赋值给最终字符串s
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
usable = usable-hdrlen-1;
if (usable > sdsTypeMaxSize(type))
usable = sdsTypeMaxSize(type);
switch(type) { // 根据类型决定对s做不同的sds hdr操作
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen); // 复制initlen的init内容到s
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}
引用 1
...December 10, 2021
What
#
docker 带来容器之风,以致容器多不胜数。如何编排和管理众多容器,使得它们同心协力办好事情,即成为了当下最大的课题。
为此,k8s 应运而生。
容器,通讯,存储,配置。
Why
#
为编排和管理数量众多的容器。
How
#
Install
#
k8s: 集群搭建所需资源
#
One or more machines running one of:
Ubuntu 16.04+
Debian 9+
CentOS 7+
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7+
Fedora 25+
HypriotOS v1.0.1+
Flatcar Container Linux (tested with 2512.3.0)
2 GB or more of RAM per machine (any less will leave little room for your apps).
2 CPUs or more.
...
December 10, 2021
第一章 可靠性、可扩展性、可维护性
#
数据密集型应用和计算密集型应用
现今很多应用程序都是 数据密集型(data-intensive) 的,而非 计算密集型(compute-intensive) 的。因此CPU很少成为这类应用的瓶颈,更大的问题通常来自数据量、数据复杂性、以及数据的变更速度。
数据密集型应用通常由标准组件构建而成,标准组件提供了很多通用的功能;例如,许多应用程序都需要:
存储数据,以便自己或其他应用程序之后能再次找到 (数据库(database))
记住开销昂贵操作的结果,加快读取速度(缓存(cache))
允许用户按关键字搜索数据,或以各种方式对数据进行过滤(搜索索引(search indexes))
向其他进程发送消息,进行异步处理(流处理(stream processing))
定期处理累积的大批量数据(批处理(batch processing))
对应可选的组件在我映像中可以有:
数据库:mysql, postgresql
缓存: redis, memcached
搜索索引: elastic search, sonic, redis search
流处理: kafka, redis stream
批处理: linux cron, golang timer
使用较小的通用组件创建了一个全新的、专用的数据系统。
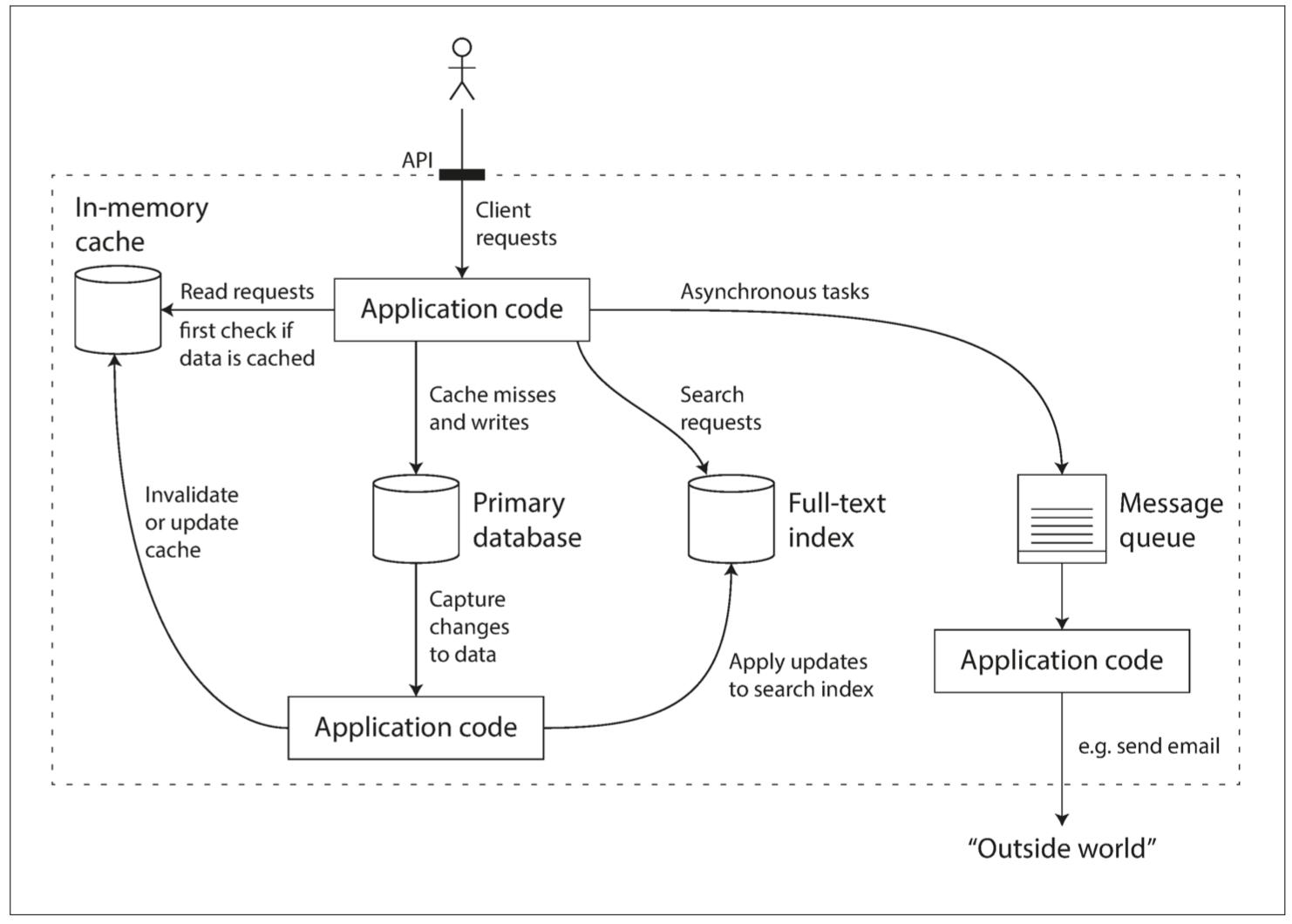
如何衡量一个系统的好坏
#
设计数据系统或服务时可能会遇到很多棘手的问题,例如:当系统出问题时,如何确保数据的正确性和完整性?当部分系统退化降级时,如何为客户提供始终如一的良好性能?当负载增加时,如何扩容应对?什么样的 API 才是好的 API?
可靠性(Reliability)
系统在困境(adversity)(硬件故障、软件故障、人为错误)中仍可正常工作(正确完成功能,并能达到期望的性能水准)。
故障通常定义为系统的一部分状态偏离其标准,而失效则是系统作为一个整体停止向用户提供服务。故障的概率不可能降到零,因此最好设计容错机制以防因故障而导致失效。
硬件错误的解决:为了减少系统的故障率,第一反应通常都是增加单个硬件的冗余度,例如:磁盘可以组建 RAID,服务器可能有双路电源和热插拔 CPU,数据中心可能有电池和柴油发电机作为后备电源,某个组件挂掉时冗余组件可以立刻接管。
软件错误的解决:仔细考虑系统中的假设和交互;彻底的测试;进程隔离;允许进程崩溃并重启;测量、监控并分析生产环境中的系统行为。
人为错误的解决:
可扩展性(Scalability)
有合理的办法应对系统的增长(数据量、流量、复杂性)
可维护性(Maintainability)
许多不同的人(工程师、运维)在不同的生命周期,都能高效地在系统上工作(使系统保持现有行为,并适应新的应用场景)。
从人的角度看:可靠就是能共困苦,同富贵;可扩展就是学习能力强,心胸广阔;可维护就是对人对己无偏见、无特例。
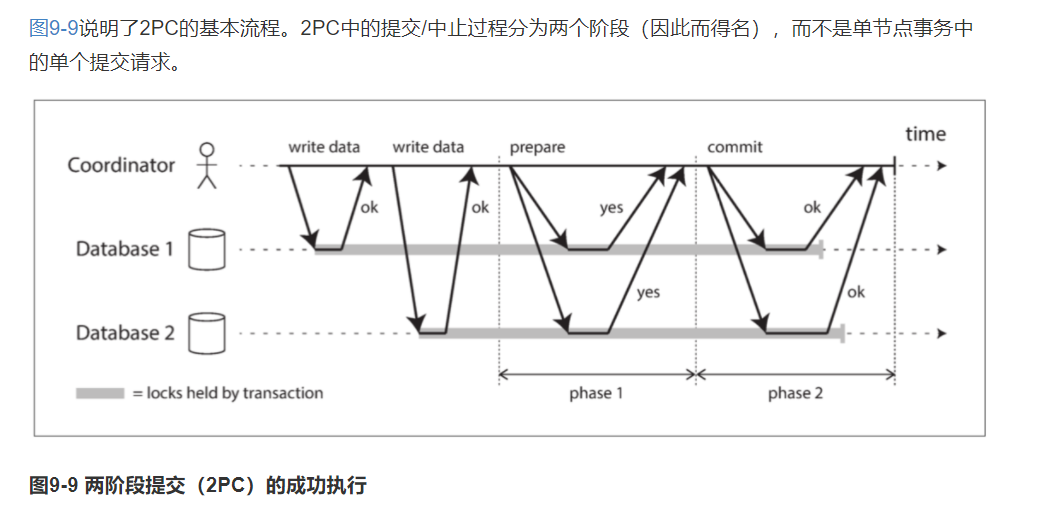
2PC(两阶段提交)
#
2PC,two-phase commit,两阶段提交。
一种用于实现跨多个节点的原子事务提交的算法,即确保所有节点提交或所有节点中止。
...December 9, 2021
虚假的 burn
#
package main
func fakeBurn() {
for {
}
}
真正的 burn
#
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"runtime"
"time"
)
var (
numBurn int
updateInterval int
)
func cpuBurn() {
for {
for i := 0; i < 2147483647; i++ {
}
// Gosched yields the processor, allowing other goroutines to run. It does not suspend the current goroutine, so execution resumes automatically.
// Gosched让当前goroutine让出处理器,从而使得其它goroutine可以运行。它不会挂起/暂停当前的goroutine,它会自动恢复执行。
runtime.Gosched()
}
}
func init() {
flag.IntVar(&numBurn, "n", 0, "number of cores to burn (0 = all)")
flag.IntVar(&updateInterval, "u", 10, "seconds between updates (0 = don't update)")
flag.Parse()
if numBurn <= 0 {
numBurn = runtime.NumCPU()
}
}
func main() {
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(numBurn)
fmt.Printf("Burning %d CPUs/cores\n", numBurn)
for i := 0; i < numBurn; i++ {
go cpuBurn()
}
// 一直执行,区别是其中一个会定期打印,另一个不会打印
if updateInterval > 0 {
t := time.Tick(time.Duration(updateInterval) * time.Second)
for secs := updateInterval; ; secs += updateInterval {
<-t
fmt.Printf("%d seconds\n", secs)
}
} else {
select {} // wait forever
}
}
December 9, 2021
首发于:简单博客
docker compose 如何访问主机服务
#
docker compose 里面的容器怎么访问主机自身起的服务呢?
20.10.0 版本在 linux 新增 host.docker.internal 支持:
docker run -it --add-host=host.docker.internal:host-gateway alpine cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
172.17.0.1 host.docker.internal # --add-host的作用就是添加了这行到/etc/hosts
172.17.0.3 cb0565ceea26
相关提交
这个 add-host 的意思是告诉容器,容器对域名 host.docker.internal 的访问都将转发到 host-gateway 去。
也就是容器内部访问这个域名 host.docker.internal 时,就会访问到对应的主机上的 host-gateway 地址。
从而达到容器访问主机上服务的效果。
那么,这个 add-host 怎么用在 compose 上呢?
在 build 里使用 extra_hosts
version: "2.3" # 因为某个bug的存在,只能用version2,不能用version3
services:
tmp:
build:
context: .
extra_hosts: # 配置extra_hosts
- "host:IP"
command: -kIL https://host
tty: true
stdin_open: true
docker compose 配置中文说明
...December 9, 2021
dbeaver: github
下载页
面向开发者、SQL 编程人员、数据库管理员和分析人员的免费的多平台数据库工具。
支持任何已有 JDBC 驱动的数据库(基本上是任何数据库)。商业版本还额外支持非 JDBC 数据源,比如:MongoDB, Cassandra, Couchbase, Redis, BigTable, DynamoDB 等。
拥有的特性:元数据编辑、SQL 编辑、富文本编辑、ER 图、数据导出/导入/转译、SQL 执行计划等。
基于 Eclipse 平台。
使用插件架构,为以下数据库提供额外功能:MySQL/MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Greenplum, Oracle, DB2 LUW, Exasol, SQL Server, Sybase/SAP ASE, SQLite, Firebird, H2, HSQLDB, Derby, Teradata, Vertica, Netezza, Informix 等。
Free multi-platform database tool for developers, SQL programmers, database administrators and analysts.
Supports any database which has JDBC driver (which basically means - ANY database). Commercial versions also support non-JDBC datasources such as MongoDB, Cassandra, Couchbase, Redis, BigTable, DynamoDB, etc. You can find the list of all databases supported in commercial versions here.
...
December 8, 2021
面向领域开发。
将业务复杂度和技术复杂度分开,逐个击破。
分离领域,各司其职。
降低复杂度,容易测试。
DDD 尝试
#
order.go:
package domain
import (
"crypto/rand"
"math/big"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
)
// 关键词:用户、店铺、商品、订单
//
// 场景描述:店铺展示商品,其价格为P、库存为N,用户(余额为Y)看到商品觉得合适,于是下单购买B个;
// 购买前,用户余额Y必须不小于P,商品库存N不小于B;购买后,用户余额减少P,库存减少B;
//
// 先不考虑并发情况,建立此时的领域模型
type User struct {
name string // 名称
phone string // 电话
balance Money // 余额
}
type Shop struct {
name string // 名称
addr string // 地址
}
type Product struct {
name string // 名称
price Money // 价格
stock int // 库存
ownShop *Shop // 所属商铺
}
type Order struct {
name string // 名称
user *User // 用户
product *Product // 商品
}
type Money int
func NewUser(name, phone string, bal Money) *User {
return &User{
name: name,
phone: phone,
balance: bal,
}
}
func (u *User) Balance() Money {
return u.balance
}
func (u *User) DeductBalance(amount Money) {
if u.balance < amount {
panic("not enough money")
}
u.balance -= amount
}
func NewShop(name, addr string) *Shop {
return &Shop{
name: name,
addr: addr,
}
}
func NewProduct(name string, price Money, stock int, shop *Shop) *Product {
return &Product{
name: name,
price: price,
stock: stock,
ownShop: shop,
}
}
func (p *Product) Stock() int {
return p.stock
}
func (p *Product) DeductStock(c int) {
if p.stock < c {
panic("not enough stock")
}
p.stock -= c
}
// NewOrder 用户对商品下单c个
func NewOrder(user *User, product *Product, c int) *Order {
name, err := GenerateRandomString(12)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
user.DeductBalance(product.price * Money(c))
product.DeductStock(c)
return &Order{
name: name,
user: user,
product: product,
}
}
func (o *Order) User() *User {
return o.user
}
func (o *Order) Product() *Product {
return o.product
}
// GenerateRandomString 随机字符串包含有数字和大小写字母
func GenerateRandomString(n int) (string, error) {
const (
letters = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
)
return generate(n, letters)
}
func generate(n int, letters string) (string, error) {
ret := make([]byte, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
num, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, big.NewInt(int64(len(letters))))
if err != nil {
return "", errors.WithStack(err)
}
ret[i] = letters[num.Int64()]
}
return string(ret), nil
}
order_test.go:
...December 7, 2021
听说读写想想干,吃喝玩乐洗洗睡。
思前想后成伟绩,轻描淡写道至理。
鹏程万里追无穷,法天象地铸有道。
生老病死自当然,功名利禄也枉然
December 2, 2021
why
#
为了将视线保持在文章上,减少构建和发布的时间占用。
what
#
github action是GitHub推出的持续集成/持续部署工具,只需要在项目中添加workflow.yml配置文件,在其中配置好任务、工作、步骤等,即可在指定动作发生时自动触发编排好的动作。换言之,如果我们在我们的博客仓库里配置了自动将内容打包和发布的workflow.yml,那我们就可以把精力集中在文章的编写,然后轻轻地提交推送,即可完成博客地打包和发布,very easy and smooth。
how
#
在github准备一个blog仓库,用于存放原始信息;再准备一个github page仓库,用于存放打包数据。
其中github page仓库已开启page,可以通过github page设置的域名访问。
我的blog仓库
我的github page仓库
workflow
#
这是我结合网络各位英豪所总结出来的一个workflow.yml配置文件
name: blog # 做什么都好,别忘了先起个平凡(kuxuan)的名字
on: # 指定触发动作
push: # 动作是:git push
branches:
- main # 指定分支: main
jobs:
build-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest # 基于ubuntu
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2 # 切换分支:git checkout
with:
submodules: recursive # Fetch Hugo themes (true OR recursive)
fetch-depth: 0 # Fetch all history for .GitInfo and .Lastmod
- name: Setup Hugo # 博客所用的打包和部署工具
uses: peaceiris/actions-hugo@v2
with:
hugo-version: latest
- name: Build # 打包
run: hugo --minify --baseURL=https://donnol.github.io # 指定base url,确保构建出来的内容里的超链接都在它里面
- name: Deploy # 部署
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
with:
deploy_key: ${{ secrets.ACTIONS_DEPLOY_KEY }} # 这个key非常关键,一言两语很难讲清楚
external_repository: donnol/donnol.github.io # 我的github page所在的仓库
PUBLISH_BRANCH: main
PUBLISH_DIR: ./public # 将本仓库的public目录下的内容提交到github page仓库
commit_message: ${{ github.event.head_commit.message }} # 提交信息
以铜为镜,可以正衣冠;以人为镜,可以明得失;
以史为镜,可以知兴替。
...

